
Special Report - FAO/WFP Markets and Food Security Assessment Mission to the Central African Republic
07/04/2014
Civil insecurity has been a serious and consistent threat to the political stability and economic development of the Central African Republic (CAR) since its independence in 1960. The economic performance of CAR has often been subpar, despite vast endowments of arable lands, dense forests, gold and diamonds, largely due to the political instability caused by poor governance, successive coups and presence of foreign militants, especially in the northeast. In 2012, CAR ranked 180 out o f 187 countries on the Human Development Index. CAR is experiencing an unprecedented crisis in terms of both magnitude and intensity following the destabilization of the former regime in December 2012 and subsequent takeover by the rebel Séléka coalition in March 2013. The country has moved from a protracted crisis, characterized by chronic underdevelopment and localized emergency situations to an acute and complex emergency affecting almost the entire population. In Decemb er 2013, an unprecedented surge in violence and chaos in the capital Bangui1 and several provinces around the country, mainly in Ouham and Ouham Pende in the North-West, exacerbated this situation. Today, CAR is on the brink of total economic and social collapse resulting in severe national and potentially regional repercussions.

Special Report - FAO/GIEWS Livestock and Market Assessment Mission to Karamoja Region, Uganda
03/04/2014
Following improved security conditions, pastoralists have returned to the pre-protected kraal system seasonal grazing patterns, being free to carry-out traditional management practices inherent to the right to roam, with consequent better access to pasture and water. • Despite a two-dekad dry spell in May-June, rainfall performance has been generally good along the season, with positive effects on grazing resources availability as confirmed by satellite-based data showing above long-term avera ge vegetation growth across the region. • Livestock body condition is generally good, with low scores only in some areas in the north with reduced pasture/water availability or with the presence of tse-tse flies. As expected, milking cows show the lowest body conditions, if compared to other classes of cattle. • Outbreaks of trypanosomosis have increased in 2013 and are likely spreading southward from the Kidepo Valley National Park, allegedly with increased movements of buffalo that carries the tse-tse flies. Other endemic diseases have often been contained by effective controlling measures. • In most markets, livestock prices showed a rising trend during the last three years and terms of trade for pastoralists have generally improved. Increasing sales of healthy animals in good body condition were noted in most markets as part of the normal livelihood strategy of local households. • There is significant demand for local animals by Ugandan traders from other districts as well as from South Sudan and Kenya. Local herders are interested in purchasing heifers, often imported from outside the region, suggesting that local herds are recovering after their decimation during the protected kraal years.
Crop Prospects and Food Situation #1, March 2014
06/03/2014
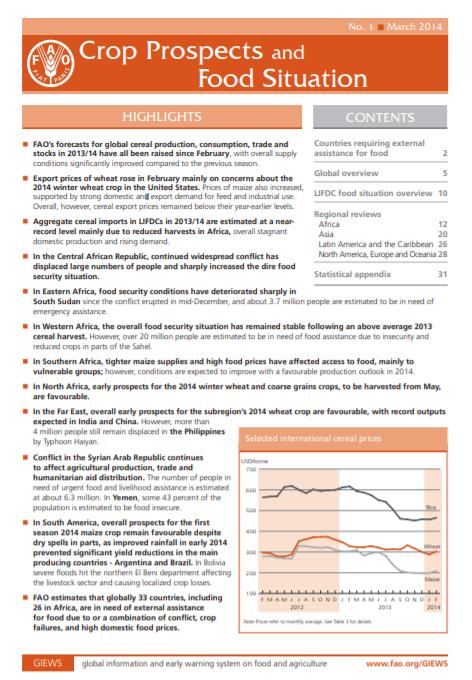
FAO’s forecasts for global cereal production, consumption, trade and stocks in 2013/14 have all been raised since February, with overall supply conditions significantly improved compared to the previous season. Export prices of wheat rose in February mainly on concerns about the 2014 winter wheat crop in the United States. Prices of maize also increased, supported by strong domestic and export demand for feed and industrial use. Overall, however, cereal export prices remained below their year-earlier levels. Aggregate cereal imports in LIFDCs in 2013/14 are estimated at a nearrecord level mainly due to reduced harvests in Africa, overall stagnant domestic production and rising demand.

Special Report - FAO/WFP Crop and Food Security Assessment Mission to South Sudan - 20 February 2014
20/02/2014
In 2013, despite the impact of floods and insecurity in some areas, generally favourable rains and absence of major outbreaks of pests and diseases favoured cereal crop production in the traditional farming sector of South Sudan. • Accordingly, total cereal harvested area in the traditional sector increased by about 2.8 percent resulting in an estimated net cereal production of about 892 000 tonnes, about 13 percent above the revised 2012 estimates and 22 percent above the average of t he previous five years. • Net cereal production from the rain-fed large and small scale mechanized sector in Upper Nile State is estimated at a reduced 57 000 tonnes due to a decline in planted area and a late onset of rains. • Livestock conditions were generally good due to adequate pasture and water availability. • Prices of locally produced cereals have declined in most markets since August 2013 and were below or around their levels in November 2012. Livestock prices, especially for small ruminants, were stable or increasing during the second half of 2013 in most markets. Terms-of-trade for pastoralists have generally improved.

Cereal supply and demand balances for sub-Saharan African countries - No.1, February 2014
13/02/2014
The FAO/GIEWS Country Cereal Balance System (CCBS) is a database of annual supply and utilization balances for main cereals, covering all countries of the world. It has been maintained by FAO/GIEWS since 1980 and is updated on a continual basis. This statistical report, which is a subset of CCBS data, presents the current-year cereal supply and demand balances for all sub-Saharan African countries, highlighting cereal import and food aid requirements of each country. This report is complement ary to the FAO/GIEWS report Crop Prospects and Food Situation and is published four times a year, with the same schedule.

No. 13 Global impacts of agricultural trade reforms. Why users need to be more vigilant when interpreting quantitative estimate
04/01/2014
There has been a recent proliferation of simulation modelling exercises attempting to quantify the potential economic gains from further liberalization of agricultural trade, and in doing so, seeking to inform the current Doha Round of multilateral trade negotiations. This paper seeks to contribute to a better appreciation of what the results of simulation models actually mean, and the extent to which they can be used to inform debates relating to trade policy reform

Challenges and opportunities of foreign investment in developing country agriculture for sustainable development
01/01/2014
This paper describes challenges, opportunities and determinants of foreign investment in developing country agriculture for sustainable development. Options and good practices for generation of mutual benefits and prevention and mitigation of risks are presented.

Countries in the Commonwealth of Independent States
01/01/2014
With the disintegration of the Soviet Union 15 new countries entered the world stage. The CIS countries are very different in size, economic structure and agricultural profile. The same is true even for the smaller group of seven CIS countries that are members of the World Trade Organization (WTO).

The changing role of multinational companies in the global banana trade
01/01/2014
Multinational trading companies, and in particular the three largest banana traders (Chiquita, Dole and del Monte), have historically played a major role in the international banana trade, exerting substantial market power in particular on the purchasing side. These vertically integrated multinational firms engage in production, purchase, transport, and marketing of bananas. They own fleet and ripening facilities, and have their own distribution networks in the importing countries, creating im portant economies of scale. The scope of their operations and their influence over the banana trade have, however, changed over time. The combined market share of the top three companies was at its highest in the 1980’s, when they controlled almost two thirds (65.3%) of global banana exports2, and the share has gradually declined since. In 2013, the market share of the top three companies was slightly over one third (36.6%) and the share of the top five companies was 44.4%, down from 70% in 2002. As a consequence, other companies now account for over half of all exports.

Impacts of foreign agricultural investment on developing countries: evidence from case studies
01/01/2014
There is growing evidence that investing in developing countries’ agricultural sector is among the most efficient ways to reduce poverty and hunger. Agricultural investments can generate a wide range of developmental benefits, but these benefits cannot be expected to arise automatically and some forms of large-scale investment carry risks for host countries. Although there has been much debate about the potential benefits and risks of international investment, there is a lack of systematic evide nce on the actual impacts on the host country and their determinants. This paper summarizes the results of FAO’s case studies on the impacts of foreign agricultural investment on host communities and countries. The studies suggest that the disadvantages of large-scale land acquisitions often outweigh the few benefits to the local community. In countries where local land rights are not clearly defined and governance is weak, large scale land acquisition raises particularly high risks for the loca l community. These include reduced access to natural resources and the loss of livelihoods, which are likely to generate local opposition to the investment. Even from the perspective of the investor, land acquisition is unlikely to be the most profitable business model due to the high potential for conflict and damage to reputation. Conversely, the studies suggest that investments that involve local farmers as equal business partners, giving them an active role and leaving them in control of the ir land, have the most positive and sustainable effects on local economies and social development. These inclusive business models need strong external support for supporting farmers and facilitating the investor-farmers relationship in order to succeed. They also require ‘patient capital’, as financial returns to investment are unlikely to materialize in the first years. Beside the business model, other important factors include the legal and institutional framework in the host country, the ter ms and conditions of the investment contract and the social and economic conditions in the investment area. Strengthening the governance and capacity of institutions in host developing countries is essential to enhancing the developmental impacts of foreign agricultural investment.

Banana market review and banana statistics 2012-2013
01/01/2014
This report is issued on an annual basis to Members and Observers of the Sub-Group on Bananas of the Intergovernmental Group on Bananas and Tropical Fruits. It is prepared by the Market and Policy Analyses of Raw Materials, Horticulture and Tropical (RAMHOT) Products Team, Trade and Market Division, FAO, Rome, and the tables contained bring together the information available to FAO, supplemented by data obtained from other sources in particular with regard to preliminary estimates.

Low Levels of Genetically Modified Crops in International Food and Feed Trade: FAO International Survey and Economic Analysis
01/01/2014
The low level presence (LLP) and adventitious presence (AP) of Genetically Modified Organisms (GMO) in internationally traded food crops have been a major issue of discussion recently. Asynchronous Approvals (AA) and zero tolerance policy have been reported to have trade diversion effects by some of the exporters. Therefore, FAO conducted a survey to evaluate the issue and examine the impact of LLP on trade flow. The survey was sent to national government organizations through FAO Representation s (FAORs), Codex contact points, and individual contacts in early 2013. Almost half of the respondents (47 percent) indicated that they produce GM crops for research or commercial use. 78 percent of respondents indicated that they have a GMO regulation; however, 22 percent either don’t have or are planning to have regulations in the future. High level of regional guidelines is a critical issue in food safety regulations worldwide. 37 percent of the respondents indicated that they have a LLP thre shold at least for one group of product (feed). The remaining 63 percent do not have any threshold limit for LLP related imports. Only 33 percent of the respondents indicated that they have a technical capacity to detect GMOs in imports.
FAO Rice Market Monitor - December 2014
01/01/2014
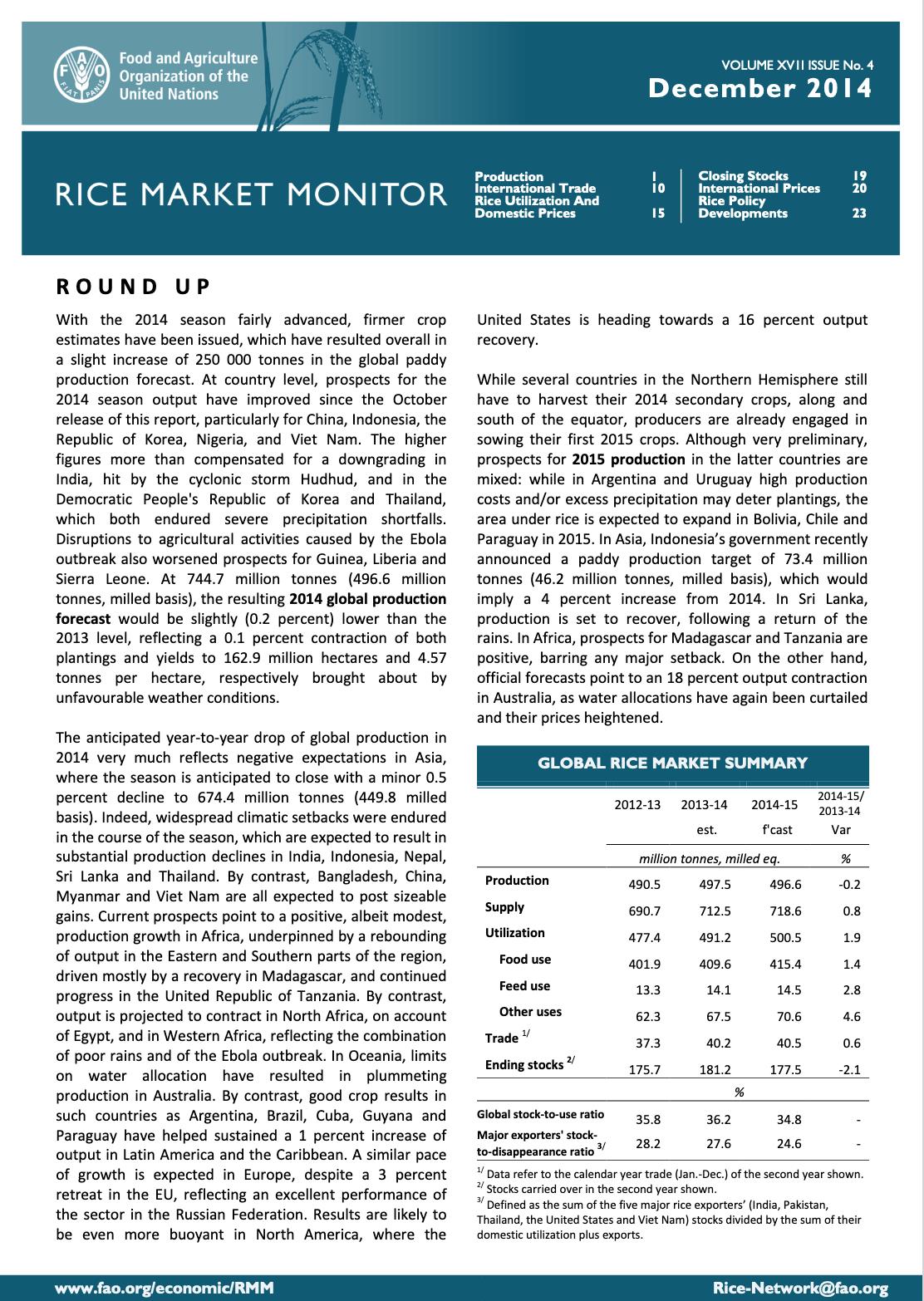
With the 2014 season fairly advanced, firmer crop estimates have been issued, which have resulted overall in a slight increase of 250 000 tonnes in the global paddy production forecast. At country level, prospects for the 2014 season output have improved since the October release of this report, particularly for China, Indonesia, the Republic of Korea, Nigeria, and Viet Nam. The higher figures more than compensated for a downgrading in India, hit by the cyclonic storm Hudhud , and in the Democra tic People's Republic of Korea and Thailand, which both endured severe precipitation shortfalls. Disruptions to agricultural activities caused by the Ebola outbreak also worsened prospects for Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone. At 744.7 million tonnes (496.6 million tonnes, milled basis), the resulting 2014 global production forecast would be slightly (0.2 percent) lower than the 2013 level, reflecting a 0. 1 percent contraction of both plantings and yields to 162.9 million hectares and 4.57 tonn es per hectare , respectively brought about by unfavourable weather conditions

Smallholder participation in the tropical superfruits value chain:ensuring equitable share of the success to enhance their livelihood
01/01/2014
The production and trade of tropical fruits generate income, improving the livelihoods and food security of producers, who are almost exclusively smallholders in developing countries. They also contribute positively to meeting daily nutritional requirements, underpinning the importance of these fruits from both a commercial and nutritional perspective. Regardless of whether they are “super” or not, value is added at each step of the value chain – from farm-gate, through intermediaries (wholesale and retail), to the consumer. Significant progress has been made to explore measures to ensure that smallholders gain fairly from value addition along the chain. However, inadequate post harvest and transport infrastructure, resource limitation, institutional support and compliance with market access requirements are some of the reasons that smallholder producers have not been fully integrated. Therefore, forming like-minded players into legal entities, such as cooperatives, would better facili tate their integration through achieving economies of scale and improving their bargaining position. In this report, supporting evidence to some of the arguments put forward will be drawn from successful projects on bananas, tropical fruits and tea which were implemented in the Dominican Republic, Mexico and Indonesia, respectively, and supervised by the RAMHOT Team of the Trade and Markets Division of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO).
Crop Prospects and Food Situation #4, December 2013
05/12/2013
Latest estimates confirm a large increase in 2013 world cereal output; early prospects for 2014 wheat crop are mostly favourable. The benchmark United States wheat export price declined in November on generally favourable 2014 crop prospects. Prices of maize and rice also eased somewhat and were at levels well below those of a year earlier. Cereal imports of LIFDCs for 2013/14 are estimated to increase by some 4 percent, mainly reflecting reduced harvests in Africa and increased demand in Egypt.

Global food price monitor - Volume 2013
05/12/2013
The Global food price monitor was issued by GIEWS from 2010 until the end of 2014, reporting on food price developments at world, regional and country level with focus on developing countries. From January 2015 this report was replaced by the Food Price Monitoring and Analysis (FPMA) Bulletin.


