Oilseeds, Oils and Meals. Monthly Price and Policy Update No.112, November 2018
13/09/2018
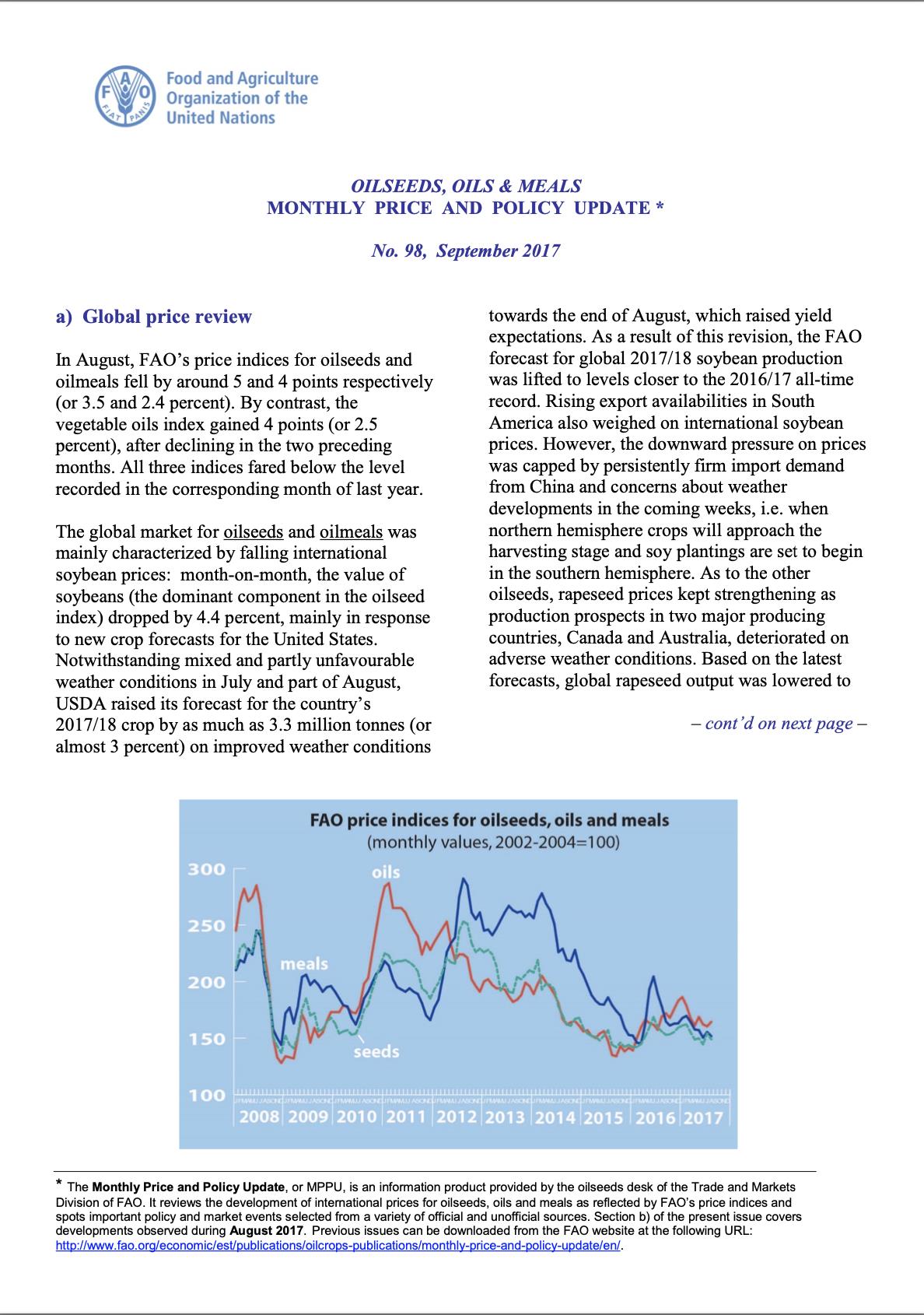
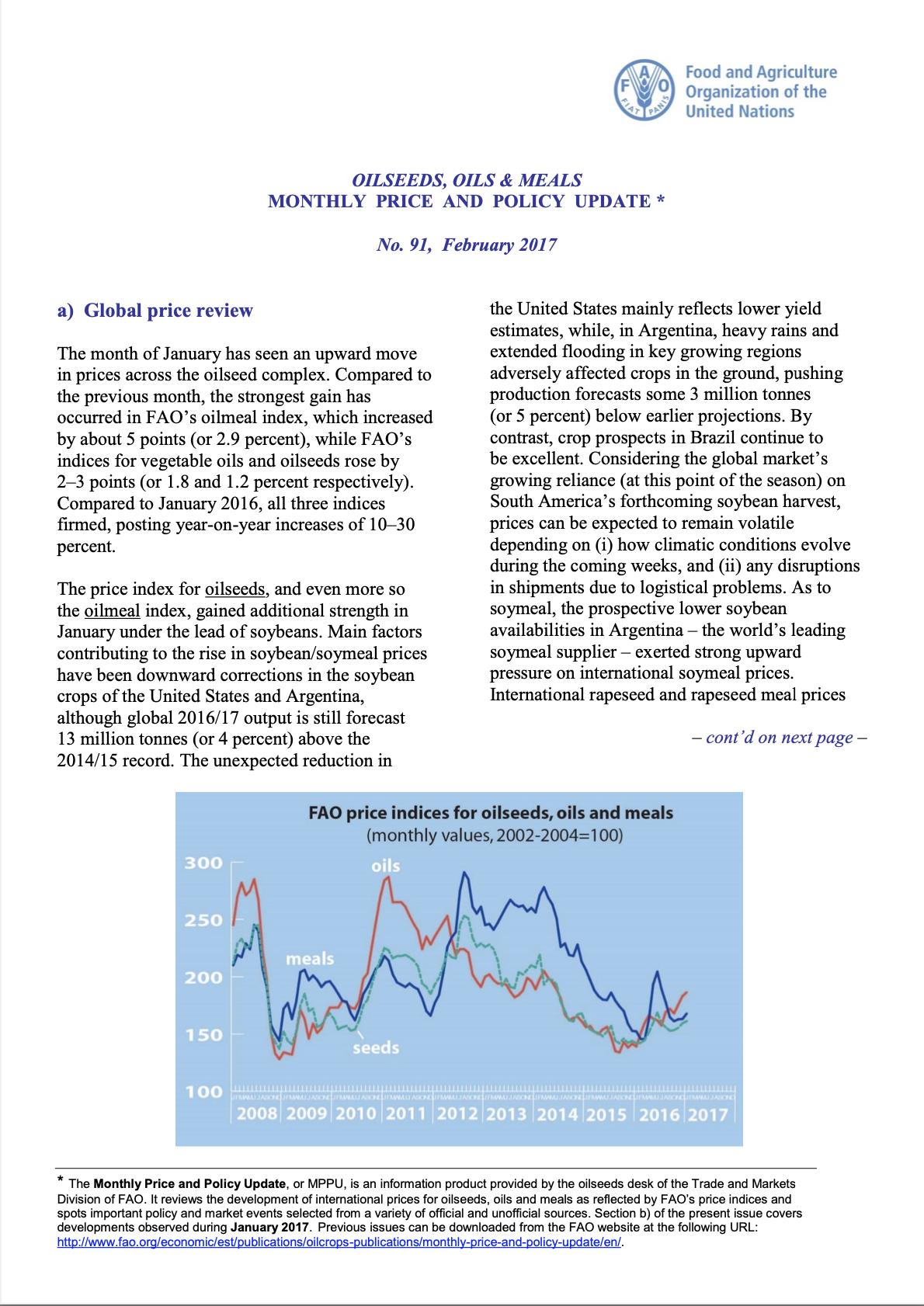
In October, FAO’s price index for oilseeds rebounded modestly from the multi-year low recorded in September, gaining 3.7 points (or 2.6 percent) but remaining below the level of the corresponding month in 2017. By contrast, the price index for vegetable oils has fallen for the ninth consecutive month, shedding 2 points (or 1.5 percent) and marking the lowest level since April 2009. The oilmeal price index remained virtually unchanged from September, staying above last year’s level.
Oilseeds, Oils and Meals. Monthly Price and Policy Update No.102, January 2018
13/09/2018
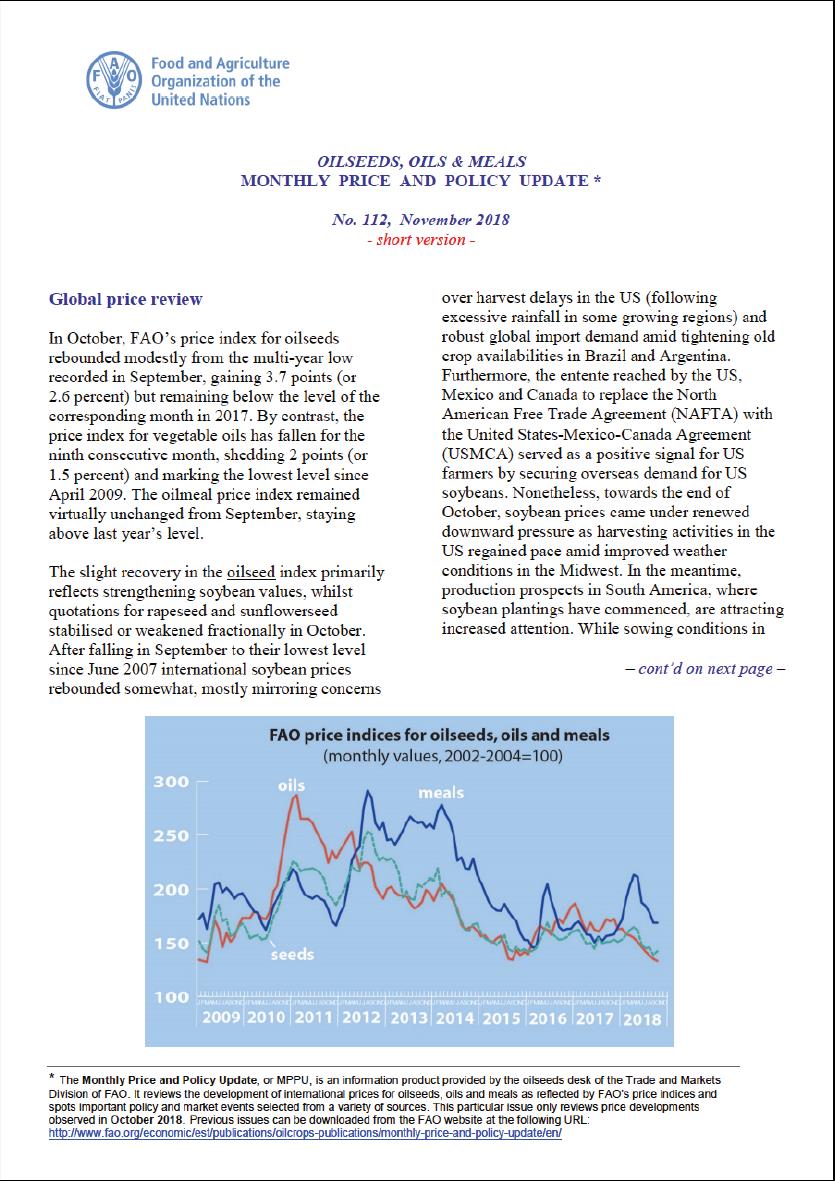
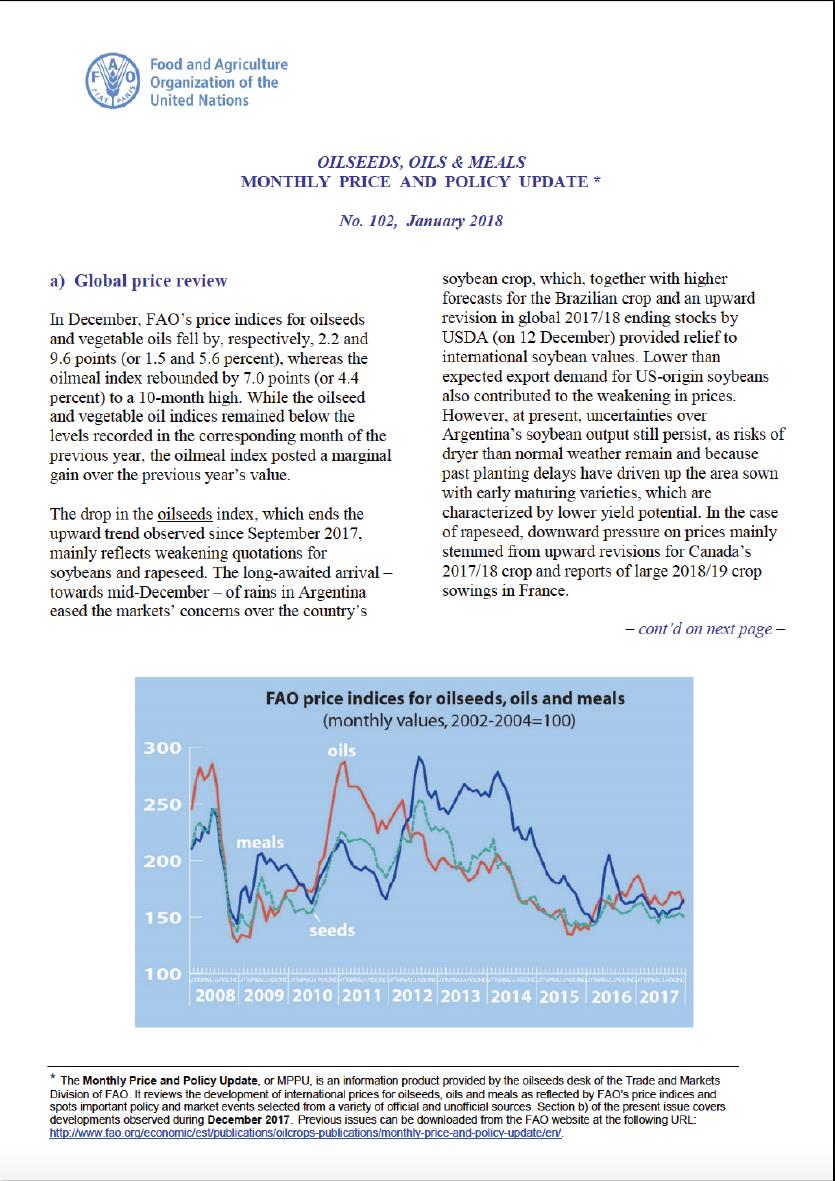
In December, FAO’s price indices for oilseeds and vegetable oils fell by, respectively, 2.2 and 9.6 points (or 1.5 and 5.6 percent), whereas the oilmeal index rebounded by 7.0 points (or 4.4 percent) to a 10-month high. While the oilseed and vegetable oil indices remained below the levels recorded in the corresponding month of the previous year, the oilmeal index posted a marginal gain over the previous year’s value.
Oilseeds, Oils and Meals. Monthly Price and Policy Update No.104, March 2018
13/09/2018
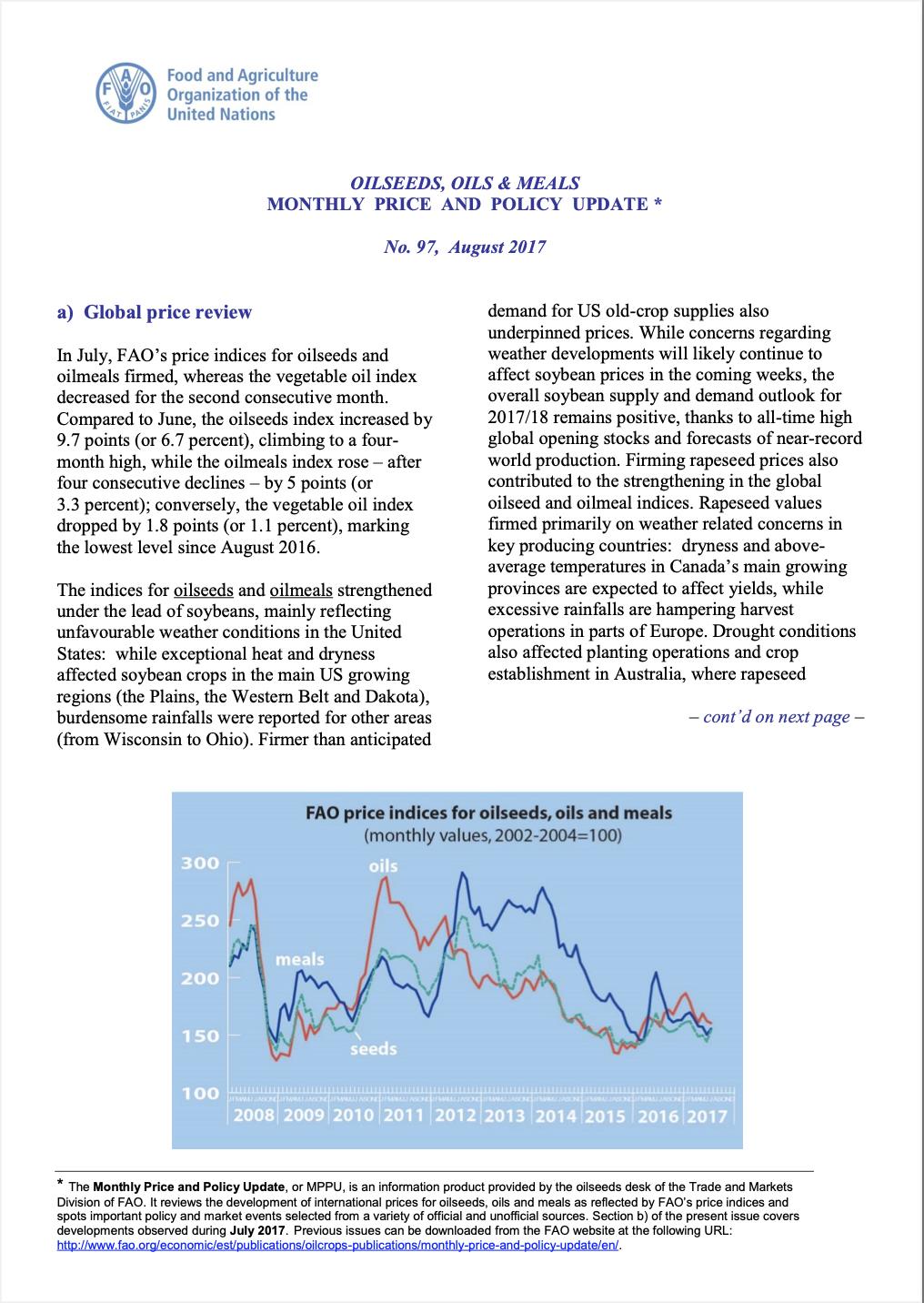
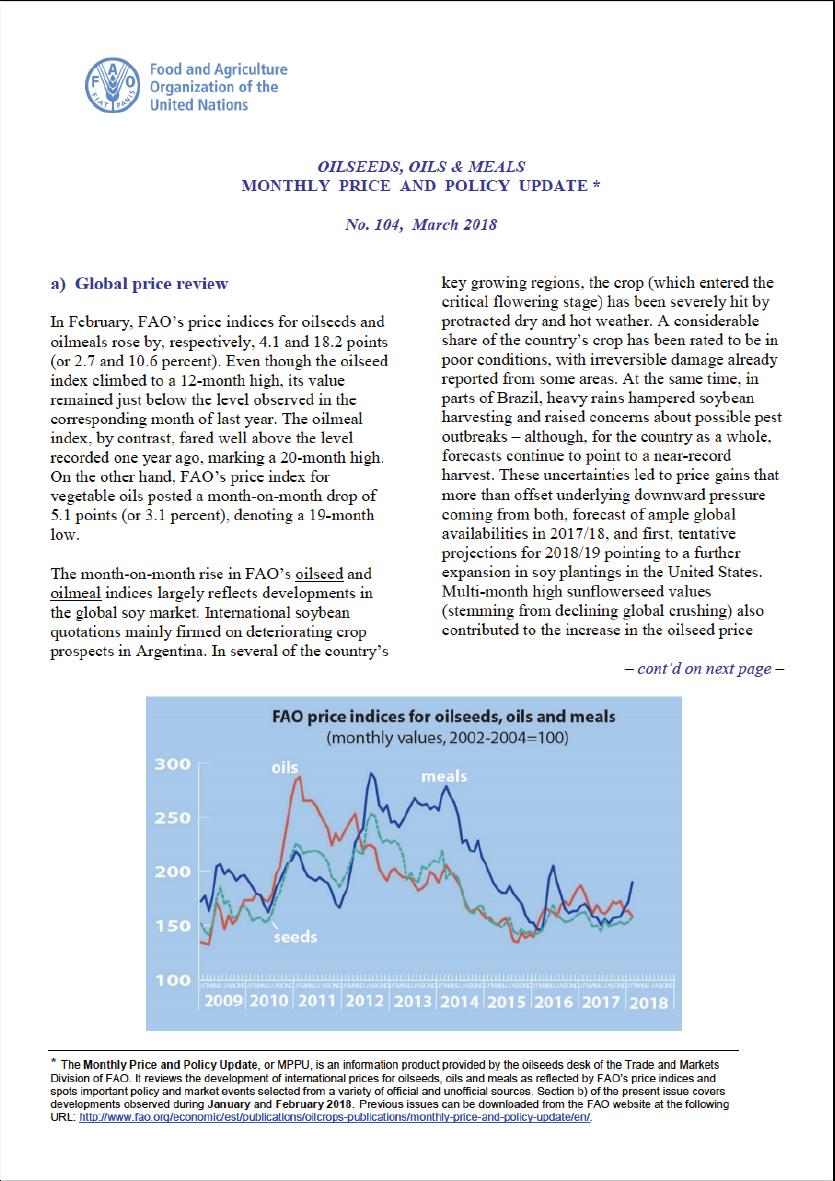
In February, FAO’s price indices for oilseeds and oilmeals rose by, respectively, 4.1 and 18.2 points (or 2.7 and 10.6 percent). Even though the oilseed index climbed to a 12-month high, its value remained just below the level observed in the corresponding month of last year. The oilmeal index, by contrast, fared well above the level recorded one year ago, marking a 20-month high. On the other hand, FAO’s price index for vegetable oils posted a month-on-month drop of 5.1 points (or 3.1 percent), denoting a 19-month low.
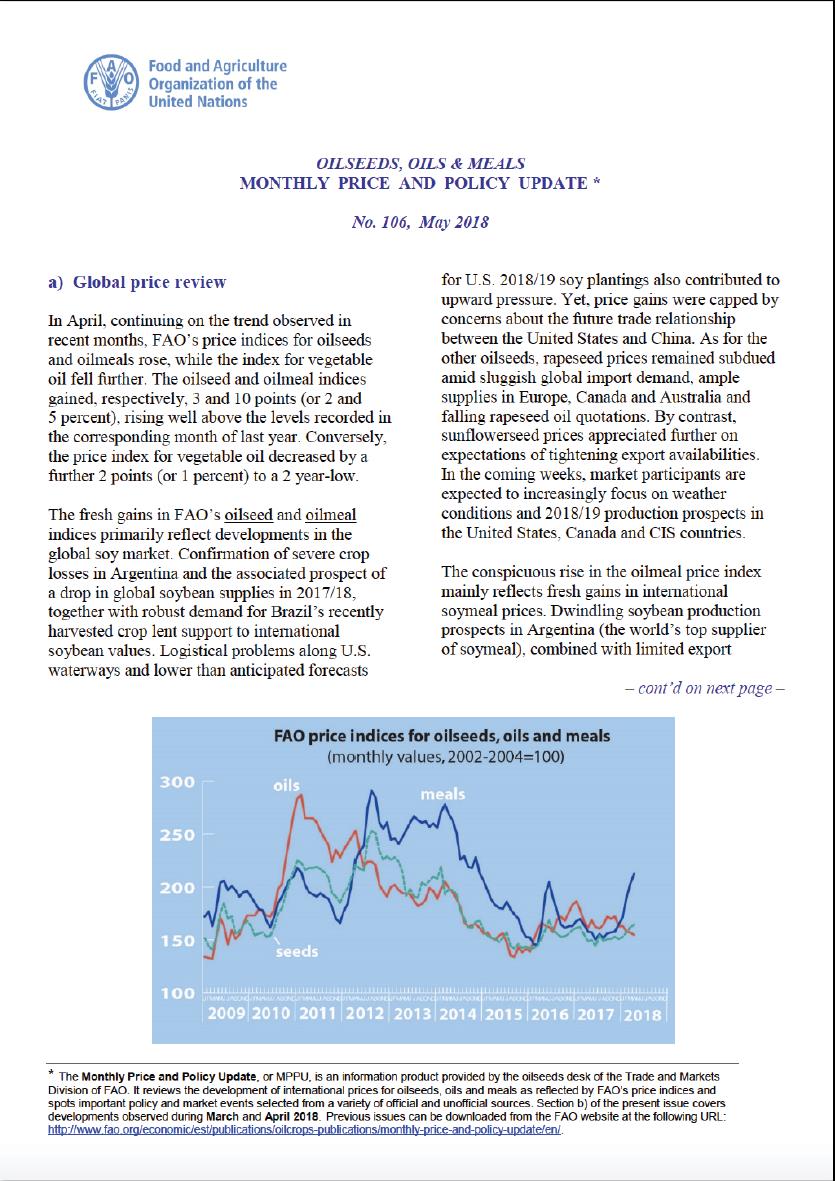
Oilseeds, Oils and Meals. Monthly Price and Policy Update No.106, May 2018
13/09/2018
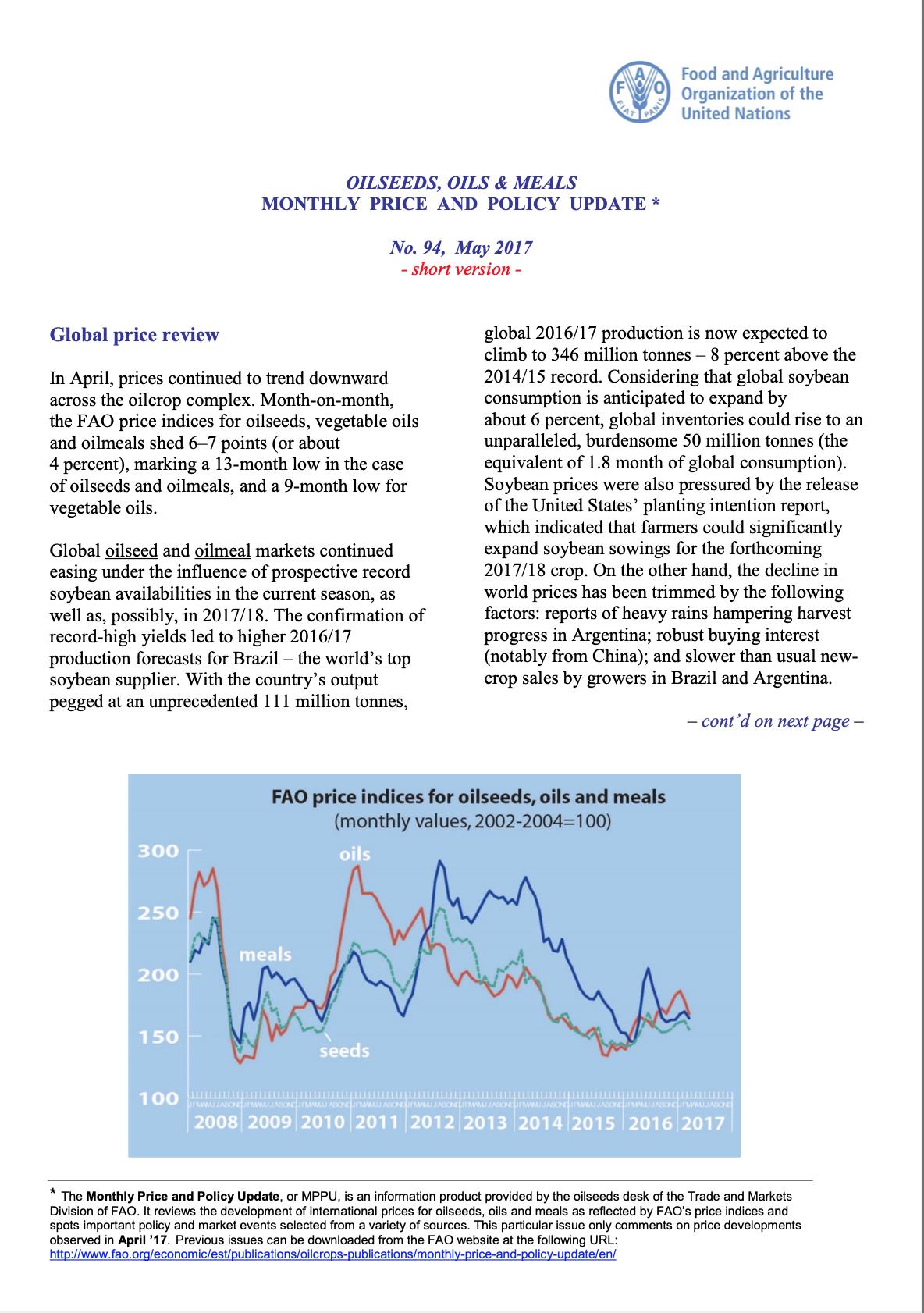
In April, continuing on the trend observed in recent months, FAO’s price indices for oilseeds and oilmeals rose, while the index for vegetable oil fell further. The oilseed and oilmeal indices gained, respectively, 3 and 10 points (or 2 and 5 percent), rising well above the levels recorded in the corresponding month of last year. Conversely, the price index for vegetable oil decreased by a further 2 points (or 1 percent) to a 2 year-low.
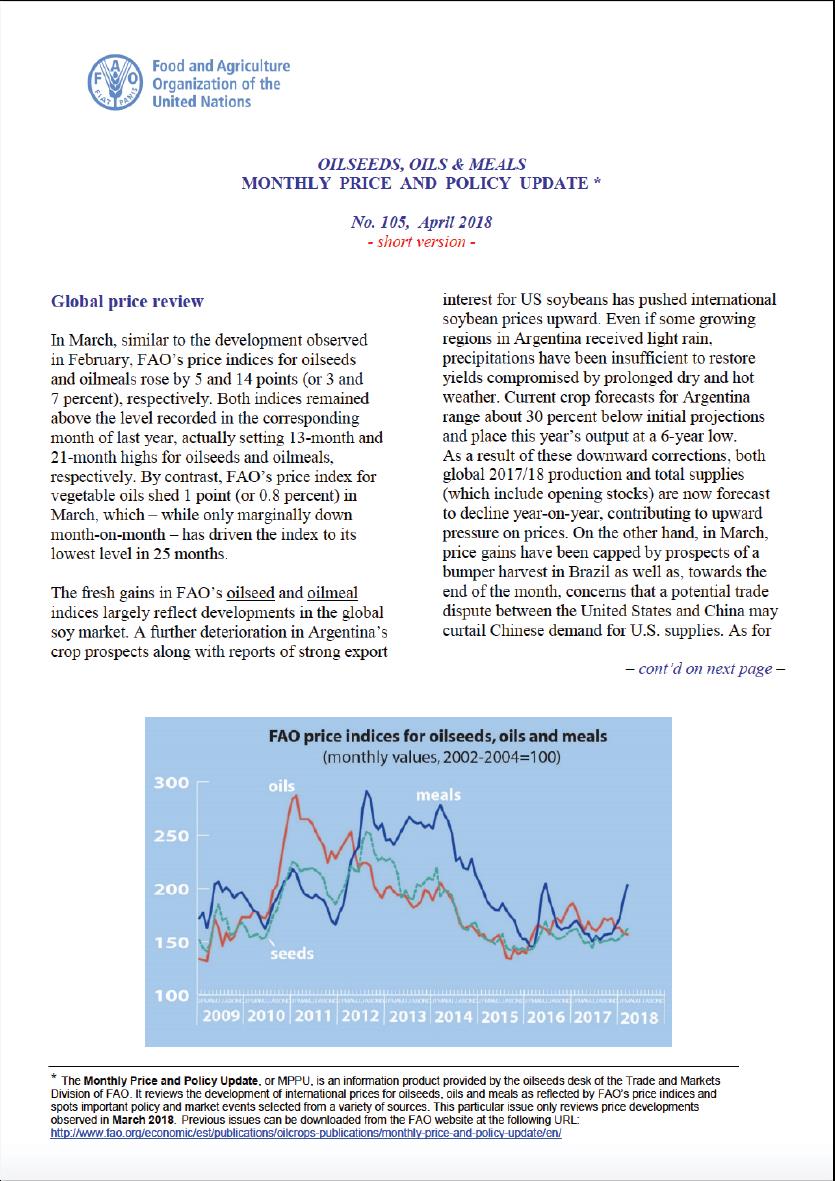
Oilseeds, Oils and Meals. Monthly Price and Policy Update No.105, April 2018
13/09/2018
In March, similar to the development observed in February, FAO’s price indices for oilseeds and oilmeals rose by 5 and 14 points (or 3 and 7 percent), respectively. Both indices remained above the level recorded in the corresponding month of last year, actually setting 13-month and 21-month highs for oilseeds and oilmeals, respectively. By contrast, FAO’s price index for vegetable oils shed 1 point (or 0.8 percent) in March, which – while only marginally down month-on-month – has driven the index to its lowest level in 25 months.

Oilcrops complex: policy changes and industry measures - Annual compendium - 2016
15/12/2017
The 2016 compendium offers an overview of salient government policies and related private sector measures concerning global and national markets for oilcrops and derived products. Its purpose is to facilitate the work of policy makers, market experts, analysts and other interested stakeholders by providing a short, concise overview of policy developments relevant to the sector. Detailed news items are presented in tabular form (in English only), preceeded by a brief discussion of the key policy trends observed in the year under review.

Oilseeds, Oils & Meals. Monthly Price and Policy Update No. 90, January 2017
01/01/2017
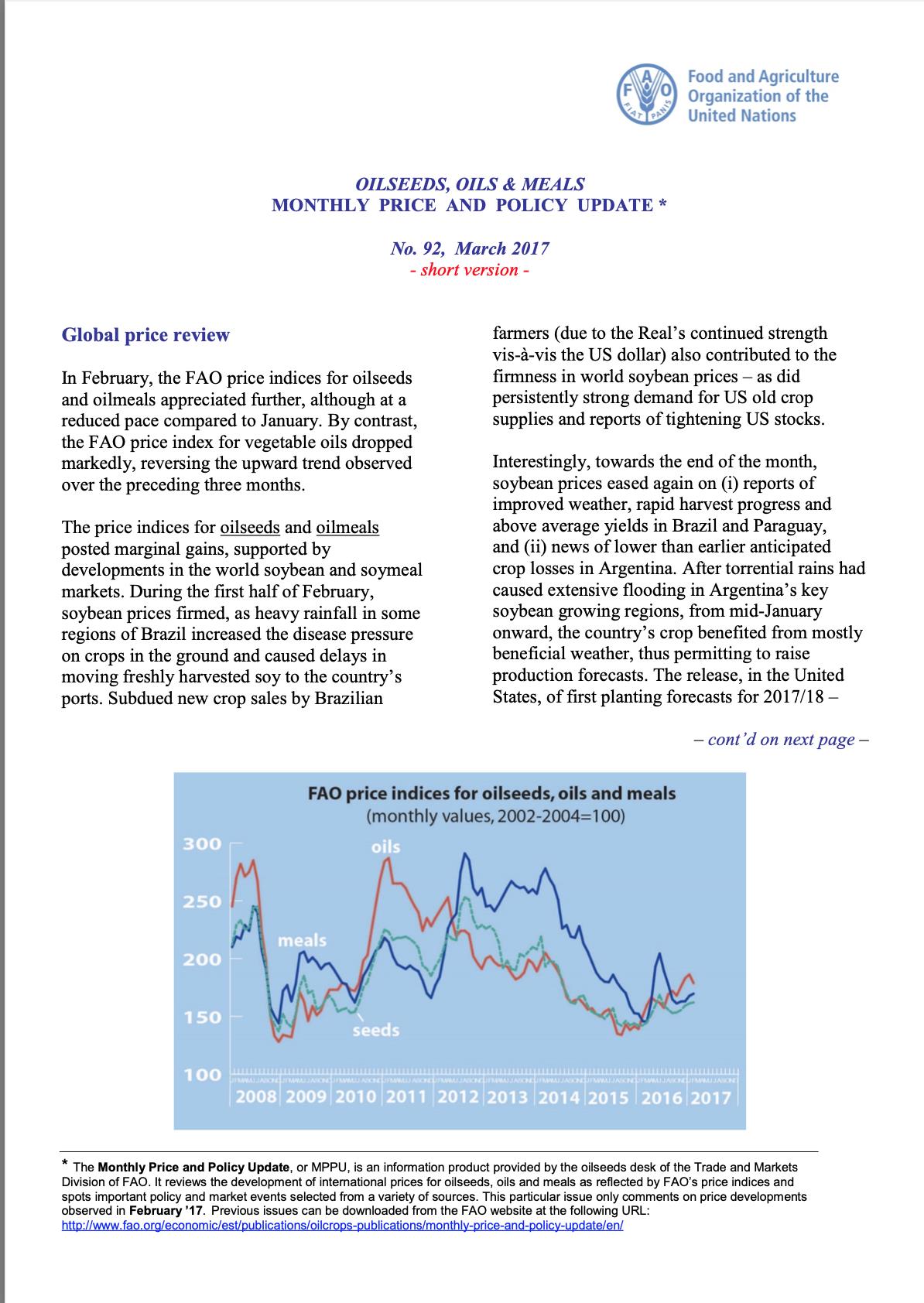
he month of August saw a rise in all threeFAO price indices trailing the oilseed complex. The oilseeds index increased for a third consecutive month, rising by 0.6 points (or 0.6 percent) and marking the highest level since January 2020. The price indices for oilmeals and vegetable oils posted more significant gains of, respectively, 3.7 and 5.5 points (or 4.6 and 5.9 percent). While all three indices fared above their year-earlier levels, the vegetable oils index stood out with its 19 percent year-on-year gain.
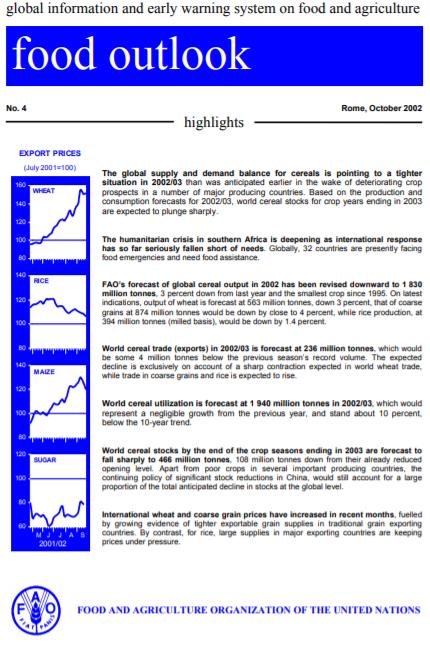
Food Outlook - October 2002
02/10/2002
The global supply and demand balance for cereals is pointing to a tighter situation in 2002/03 than was anticipated earlier in the wake of deteriorating crop prospects in a number of major producing countries. Based on the production and consumption forecasts for 2002/03, world cereal stocks for crop years ending in 2003 are expected to plunge sharply. The humanitarian crisis in southern Africa is deepening as international response has so far seriously fallen short of needs. Globally, 32 countries are presently facing food emergencies and need food assistance. FAO’s forecast of global cereal output in 2002 has been revised downward to 1 830 million tonnes, 3 percent down from last year and the smallest crop since 1995. On latest indications, output of wheat is forecast at 563 million tonnes, down 3 percent, that of coarse grains at 874 million tonnes would be down by close to 4 percent, while rice production, at 394 million tonnes (milled basis), would be down by 1.4 percent. World cereal trade (exports) in 2002/03 is forecast at 236 million tonnes, which would be some 4 million tonnes below the previous season’s record volume. The expected decline is exclusively on account of a sharp contraction expected in world wheat trade, while trade in coarse grains and rice is expected to rise. World cereal utilization is forecast at 1 940 million tonnes in 2002/03, which would represent a negligible growth from the previous year, and stand about 10 percent, below the 10-year trend. World cereal stocks by the end of the crop seasons ending in 2003 are forecast to fall sharply to 466 million tonnes, 108 million tonnes down from their already reduced opening level. Apart from poor crops in several important producing countries, the continuing policy of significant stock reductions in China, would still account for a large proportion of the total anticipated decline in stocks at the global level. International wheat and coarse grain prices have increased in recent months, fuelled by growing evidence of tighter exportable grain supplies in traditional grain exporting countries. By contrast, for rice, large supplies in major exporting countries are keeping prices under pressure. FOOD AND AGRICULTUR
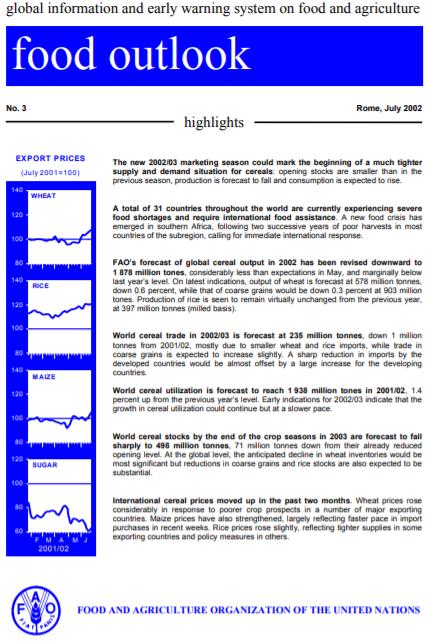
Food Outlook - July 2002
02/07/2002
The new 2002/03 marketing season could mark the beginning of a much tighter supply and demand situation for cereals: opening stocks are smaller than in the previous season, production is forecast to fall and consumption is expected to rise. A total of 31 countries throughout the world are currently experiencing severe food shortages and require international food assistance. A new food crisis has emerged in southern Africa, following two successive years of poor harvests in most countries of the subregion, calling for immediate international response. FAO’s forecast of global cereal output in 2002 has been revised downward to 1 878 million tones, considerably less than expectations in May, and marginally below last year’s level. On latest indications, output of wheat is forecast at 578 million tonnes, down 0.6 percent, while that of coarse grains would be down 0.3 percent at 903 million tones. Production of rice is seen to remain virtually unchanged from the previous year, at 397 million tonnes (milled basis). World cereal trade in 2002/03 is forecast at 235 million tonnes, down 1 million tonnes from 2001/02, mostly due to smaller wheat and rice imports, while trade in coarse grains is expected to increase slightly. A sharp reduction in imports by the developed countries would be almost offset by a large increase for the developing countries. World cereal utilization is forecast to reach 1 938 million tones in 2001/02, 1.4 percent up from the previous year’s level. Early indications for 2002/03 indicate that the growth in cereal utilization could continue but at a slower pace. World cereal stocks by the end of the crop seasons in 2003 are forecast to fall sharply to 498 million tonnes, 71 million tonnes down from their already reduced opening level. At the global level, the anticipated decline in wheat inventories would be most significant but reductions in coarse grains and rice stocks are also expected to be substantial. International cereal prices moved up in the past two months. Wheat prices rose considerably in response to poorer crop prospects in a number of major exporting countries. Maize prices have also strengthened, largely reflecting faster pace in import purchases in recent weeks. Rice prices rose slightly, reflecting tighter supplies in some exporting countries and policy measures in others.