Responsible investment and COVID-19: Addressing impacts, risks and responsible business conduct in agricultural value chains
19/11/2020
The COVID-19 pandemic has generated serious threats to food security and nutrition and has greatly affected livelihoods and working conditions in agricultural value chains. This policy brief focuses on the role of responsible investment and responsible business conduct along agricultural value chains in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic. It provides policy recommendations for governments, investors, enterprises and civil society on how they can encourage responsible investment and responsible business conduct in agriculture in these challenging times.
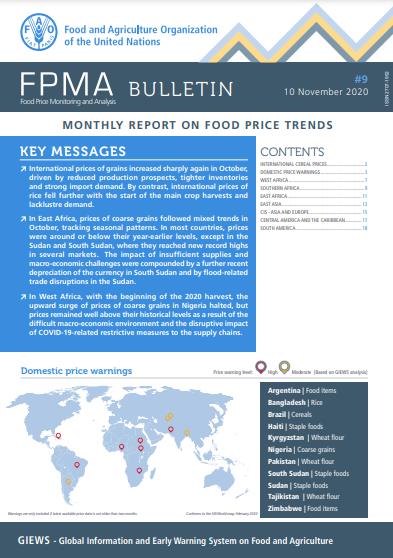
Food Price Monitoring and Analysis (FPMA) Bulletin # 9, 10 November 2020
10/11/2020
International prices of grains increased sharply again in October, driven by reduced production prospects, tighter inventories and strong import demand. By contrast, international prices of rice fell further with the start of the main crop harvests and lacklustre demand. In East Africa, prices of coarse grains followed mixed trends in October, tracking seasonal patterns. In most countries, prices were around or below their year-earlier levels, except in the Sudan and South Sudan, where they reached new record highs in several markets. The impact of insufficient supplies and macro‑economic challenges were compounded by a further recent depreciation of the currency in South Sudan and by flood‑related trade disruptions in the Sudan. In West Africa, with the beginning of the 2020 harvest, the upward surge of prices of coarse grains in Nigeria halted, but prices remained well above their historical levels as a result of the difficult macro-economic environment and the disruptive impact of COVID-19-related restrictive measures to the supply chains.

Major tropical fruits - Statistical compendium 2019
09/11/2020
The Major Tropical Fruits Statistical compendium, issued once a year, contains information on global trade in mangoes, pineapples, avocados and papayas. Its sources include information provided by FAO member nations, traders, news bulletins and the opinions of commodity specialists and represents the most authoritative and up-to-date source of information on the world tropical fruit economy.

In Brief to The State of Agricultural Commodity Markets 2020
31/10/2020
The In Brief version of the FAO flagship publication, The State of Agricultural Commodity Markets 2020, contains the key messages and main points from the publication and is aimed at the media, policy makers and a more general public.

The State of Agricultural Commodity Markets 2020
31/10/2020
The State of Agricultural Commodity Markets 2020 (SOCO 2020) aims to discuss policies and mechanisms that promote sustainable outcomes – economic, social and environmental – in agricultural and food markets, both global and domestic. The analysis is organized along the trends and challenges that lie at the heart of global discussions on trade and development.
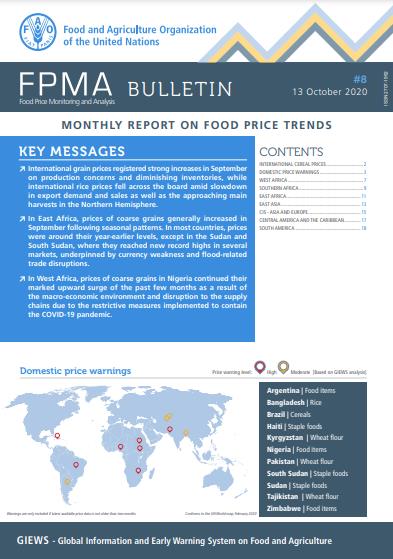
Food Price Monitoring and Analysis (FPMA) Bulletin # 8, 13 October 2020
13/10/2020
International grain prices registered strong increases in September on production concerns and diminishing inventories, while international rice prices fell across the board amid slowdown in export demand and sales as well as the approaching main harvests in the Northern Hemisphere. In East Africa, prices of coarse grains generally increased in September following seasonal patterns. In most countries, prices were around their year-earlier levels, except in the Sudan and South Sudan, where they reached new record highs in several markets, underpinned by currency weakness and flood-related trade disruptions. In West Africa, prices of coarse grains in Nigeria continued their marked upward surge of the past few months as a result of the macro-economic environment and disruption to the supply chains due to the restrictive measures implemented to contain the COVID-19 pandemic.

Innovative business models for small farmer inclusion
09/10/2020
Farmer participation in agricultural markets is of major importance for rural economic growth and poverty alleviation in developing countries. This paper discusses market failures and constraints in agriculture in low-income countries, focusing on how these failures and constraints affect small farmers, input sellers and output buyers.

The effects of global value chain (GVC) participation on the economic growth of the agricultural and food sectors
09/10/2020
Trade liberalization has long been advocated as a means to foster growth and welfare. In developing countries, the expansion of global value chain (GVC) participation of agriculture and food sectors could support transformation from a subsistence-oriented and farm-centered system to a commercialized, productive and off-farm centered one.

Competition, market power, surplus creation and rent distribution in agri-food value chains
09/10/2020
This paper reviews competition issues in agro-food value chains, including forms of governance and organization, concentration and market power and private standards implications. The paper discusses different value chains in food and agriculture and analyses how services and technologies are embedded in the final value and assesses the share of the different value chain segments.

The convergence of food diets: Characterizing consumption patterns, food diversity, and the relationship to trade
09/10/2020
Since the 1990s, technological advancements, growing incomes, increased trade, and urbanization have significantly impacted consumption patterns. Worldwide, there is growing evidence of some convergence of diets being facilitated by rapid changes in global food systems including the increasing market share held by supermarkets at all income levels. The formation of the World Trade Organization (WTO) and the emergence and rapid spread of the Internet have also played important roles in facilitating trade and increasing the variety of food available to consumers. Empirical evidence to examine these impacts has mostly been gathered at the household level and, at the global level, the focus has been on the effect of globalization on obesity and health. Using data from the periods 1994–1996 (WTO formation and emergence of the Internet) and 2015–2017 (rapid spread of the Internet), this paper analyses whether global diets are, in fact, converging. In the comparison of these two periods, the author finds that, as trade intensity increases for cereals, sugars, vegetable oils, and meat – which account for more than two-thirds of calories consumed – so does diversity of products consumed from within each group. The relationship between greater trade intensity and caloric consumption diversity is strongest for cereals, meat, and sugars. The author suggests that further research should undertake a disaggregated trade analysis in order to understand whether the increased food diversity is coming from imports of more diverse foods or other factors.

Mapping global value chain (GVC) participation, positioning and vertical specialization in agriculture and food
09/10/2020
This Technical Report includes: • A policy note with: 1) a short review of the literature on the state-of-art methodologies for computing indicators for global value chain (GVC) participation, positioning and vertical specialization; and 2) a mapping and short analysis of agriculture and food GVCs by world region.

A quantitative analysis of trends in agricultural and food global value chains (GVCs)
09/10/2020
Over the last decade, increasing international fragmentation of production has affected both trade and production: these activities have become increasingly organized around what is commonly referred to as global value chains (GVCs). Increased fragmentation has brought with it challenges of tracing and measuring international divisions of labor, value-added, and so forth. In fact, conventional measures of trade only measure the gross value of exchanges between partners.

Assessing the impact of trade and other policies on global value chain (GVC) participation, positioning and vertical specialization in agriculture and food
09/10/2020
This technical paper includes: A literature review of the impact of trade policies and domestic support measures (for example, subsidies) on global value chain (GVC) participation including the effects of tariffs and non-tariff measures, Regional Trade Agreements (RTAs) and Rules of Origin, as well as recent market developments and trade tensions on GVC linkages.

COVID-19: Channels of transmission to food and agriculture
05/10/2020
FAO is analysing and providing updates on the emerging COVID-19 pandemic’s effects on agricultural markets—effects that are still largely unknown. Most current assessments generally foresee a contraction in both supply of and demand for agricultural products, and point to possible disruptions in trade and logistics. On the supply side, widely different views remain on the duration of the shocks, the price dynamics, differential impacts between domestic and international markets, differences across countries and commodities, the likely paths of recovery, and the policy actions to remedy the various shock waves. On the demand side, there is near ubiquitous agreement that agricultural demand and trade would slow-down, with contractions stemming from a deceleration in overall economic activity (GDP growth) and rising rates of unemployment. While food and agricultural systems are exposed to both demand and supply side shocks (symmetric), these shocks are not expected to take place in parallel (asynchronous) since, inter alia, consumers can draw on savings, food stocks and safety nets.

Special Report – FAO Mission to Assess the Impact of the Financial Crisis on Agriculture in the Republic of Lebanon
21/09/2020
At the request of the Ministry of Agriculture (MoA) and in collaboration with the appropriate Government agencies, an FAO assessment Mission visited Lebanon between 2 and 13 February 2020 to conduct an examination of the impact of the economic and financial crisis on the domestic agricultural sector. The Mission put forward recommendations for appropriate actions to be taken by the Government and the international community to minimize the negative impacts of the crisis on the sector as well as agricultural livelihoods and to protect the most vulnerable in the immediate term.

Agricultural value chains and social and environmental impacts: Trends, challenges, and policy options
19/09/2020
With the global population approaching 8 billion, the role of agricultural value chains (VCs) is increasingly important in ensuring sustainable and equitable food production. However, in developing countries, market failures can prevent small farmers from fully participating in domestic and global value chains, and issues related to climate change create further challenges.

Digital technology and agricultural markets
19/09/2020
Digital technologies have a high potential to enable further development of the agricultural sector, significantly reshape food value chains (FVCs), and greatly contribute towards more productive, resilient and transparent food systems. This paper provides a non-technical overview of digital technologies that have a high potential to revolutionize the agriculture and food industry, and contribute towards inclusion of small farmers into FVCs.

Cereal supply and demand balances for sub-Saharan African countries - No.3, September 2020
17/09/2020
The FAO/GIEWS Country Cereal Balance System (CCBS) is a database of annual supply and utilization balances for main cereals, covering all countries of the world. Since 1980, the FAO/GIEWS Team maintains and updates it continually. This statistical report contains a subset of CCBS data and presents updated cereal supply and demand balances for all sub-Saharan African countries. It complements the information of the FAO/GIEWS Crop Prospects and Food Situation report and is published four time a year with the same schedule.