Crop Prospects and Food Situation - Quarterly Global Report, No. 3, September 2020
17/09/2020
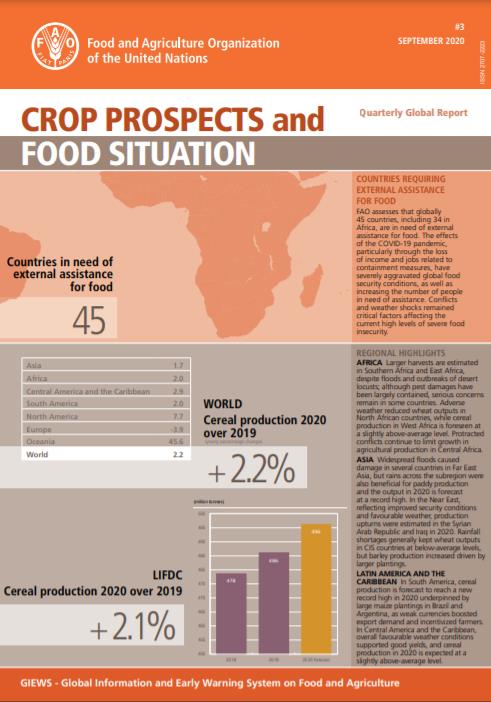
FAO assesses that globally 45 countries, including 34 in Africa, are in need of external assistance for food. The effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, particularly through the loss of income and jobs related to containment measures, have severely aggravated global food security conditions, as well as increasing the number of people in need of assistance. Conflicts and weather shocks remained critical factors affecting the current high levels of severe food insecurity.
Oilseeds, Oils & Meals. Monthly Price and Policy Update No.134, September 2020
16/09/2020
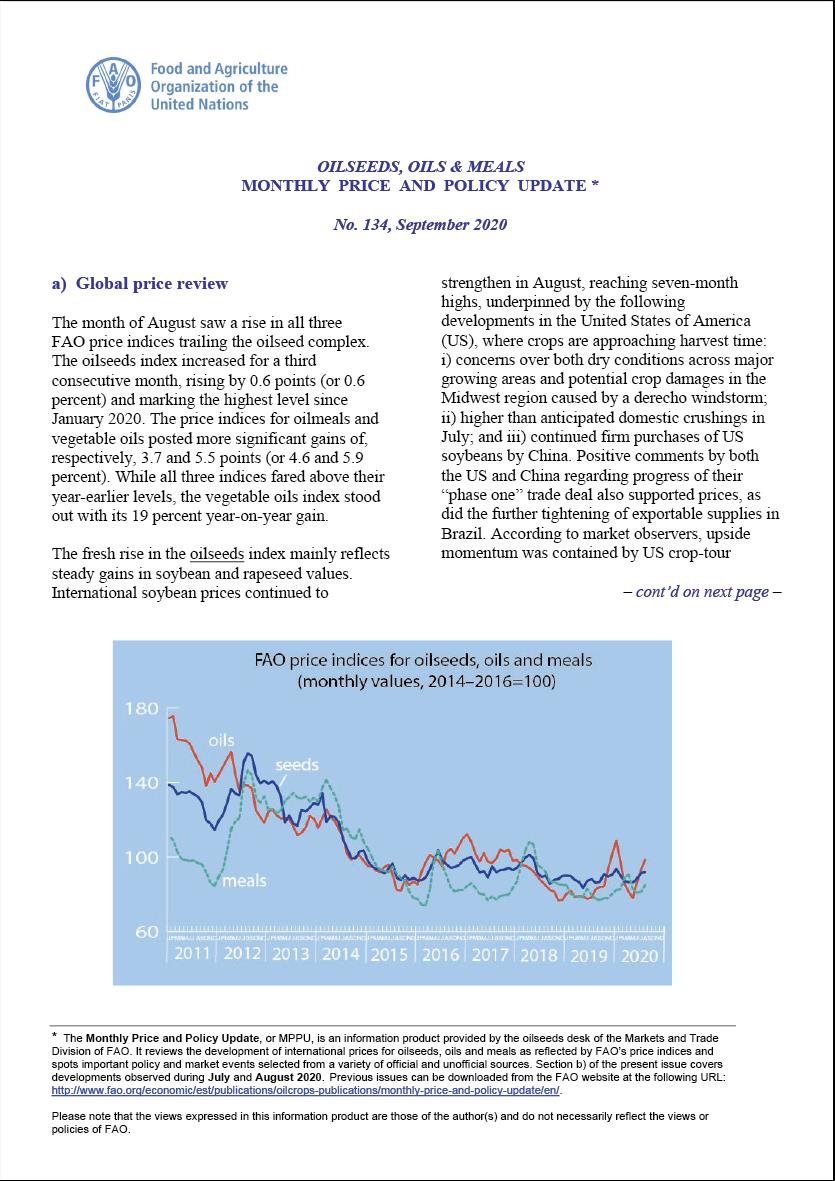
The month of August saw a rise in all threeFAO price indices trailing the oilseed complex. The oilseeds index increased for a third consecutive month, rising by 0.6 points (or 0.6 percent) and marking the highest level since January 2020. The price indices for oilmeals and vegetable oils posted more significant gains of, respectively, 3.7 and 5.5 points (or 4.6 and 5.9 percent). While all three indices fared above their year-earlier levels, the vegetable oils index stood out with its 19 percent year-on-year gain.

Trade and Sustainable Development Goal 2 – Policy options and their trade-offs
13/09/2020
With trade recognized as a means of implementation under Agenda 2030, policy-makers will need to ensure that trade, and policies affecting trade and markets, are taken into consideration as part of their efforts to achieve SDG 2. The five targets that set out the level and ambition of SDG 2 (ending hunger; ending all forms of malnutrition; doubling the agricultural productivity and incomes of small-scale food producers; ensuring sustainable food production systems; and maintaining genetic diversity), as well as trade itself, often constitute distinct policy priorities for governments. Trade and related policy measures that may be designed to achieve one target can potentially have unintended negative consequences that undermine the achievement of other targets, both within the country where the measure is applied and in the trading partner countries. It is therefore important that policy-makers identify and recognize areas in which difficult tradeoffs may be needed between competing policy objectives, and identify possible ways in which these can be addressed. Furthermore, while the different targets set out under SDG 2 are mutually interdependent and inter-related, it is important to address the trade policy dimension of each component individually as part of a broader plan of action.

Recent trends and prospects in the world cotton market and policy developments
12/09/2020
The cotton sector contributes significantly to the economies of a number of developing countries, as well as to the livelihoods of millions of rural smallholders worldwide. In 2019, world production of cotton was valued at about USD 46 billion, while global trade reached USD 15 billion. Moreover, the cotton industry employs an estimated 150 million people across 75 countries, making the cotton sector an important contributor to the achievements of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Understanding the drivers of the cotton market and identifying the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead is key, given the socio-economic significance of the sector. The mobilisation of innovative technologies and resources is vital to ensure that the sector remains viable and sustainable. As FAO Director-General QU Dongyu highlighted during the World Cotton Day event held at the WTO headquarters in October 2019, it is critical that the sector meets the highest standards of sustainability at all stages of the value chain. It is time to do things differently: to explore innovative approaches and new ideas aimed at pro-poor outcomes.

Major tropical fruits - Market Review 2019
11/09/2020
The Major Tropical Fruits Market Review is issued on an annual basis to Members and Observers of the Sub-Group on Tropical Fruits of the Intergovernmental Group on Bananas and Tropical Fruits and offers an overview of recent developments in international trade in mangoes, pineapples, avocados, and papayas.

No. 36 The role of digital technologies in livestock traceability and trade
10/09/2020
This policy brief provides an overview on the role of digital technologies in optimizing traceability in trade for animals and animal products. It highlights the ways in which digital technologies can the enhance performance for monitoring and controlling animal disease, managing food safety and fraud risks, complying with animal production and food standards, facilitating trade and raising consumer awareness.
Food Price Monitoring and Analysis (FPMA) Bulletin # 7, 10 September 2020
10/09/2020
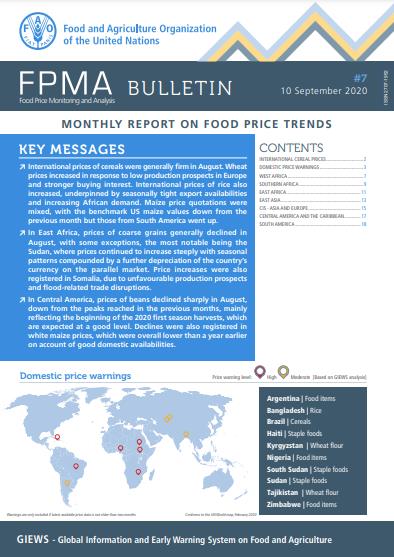
International prices of cereals were generally firm in August. Wheat prices increased in response to low production prospects in Europe and stronger buying interest. International prices of rice also increased, underpinned by seasonally tight export availabilities and increasing African demand. Maize price quotations were mixed, with the benchmark US maize values down from the previous month but those from South America went up. In East Africa, prices of coarse grains generally declined in August, with some exceptions, the most notable being the Sudan, where prices continued to increase steeply with seasonal patterns compounded by a further depreciation of the country’s currency on the parallel market. Price increases were also registered in Somalia, due to unfavourable production prospects and flood‑related trade disruptions. In Central America, prices of beans declined sharply in August, down from the peaks reached in the previous months, mainly reflecting the beginning of the 2020 first season harvests, which are expected at a good level. Declines were also registered in white maize prices, which were overall lower than a year earlier on account of good domestic availabilities.

Food Outlook - May 2020
08/09/2020
Food markets will face many more months of uncertainty related to the COVID-19 pandemic. However, while most markets are braced for a major global economic downturn, the agri-food sector is likely to display more resilience to the crisis than other sectors. Food Outlook is published by the Trade and Markets Division of FAO under Global Information and Early Warning System (GIEWS). It is a biannual publication focusing on developments affecting global food and feed markets. Each report provides comprehensive assessments and short term forecasts for production, utilization, trade, stocks and prices on a commodity by commodity basis and includes feature articles on topical issues. Food Outlook maintains a close synergy with another major GIEWS publication, Crop Prospects and Food Situation, especially with regard to the coverage of cereals. Food Outlook is available in English. The summary section is also available in Arabic, Chinese, French, Russian and Spanish.

Food Outlook - November 2020
05/09/2020
As it was projected earlier in the year, while most markets were braced for a major global economic downturn, the food sector, including markets for bananas and tropical fruits, continued to display more resilience to the Covid-19 pandemic than other sectors. This report provides supply and demand forecasts for basic foodstuffs, fish and fishery products along with price analysis, policy information and a preliminary assessment of the impacts of the Covid-19 pandemic on trade in bananas and tropical fruits. The report’s special feature reviews recent trends in food imports bills and export earnings. Food Outlook is published by the Markets and Trade Division of FAO as part of the Global Information and Early Warning System (GIEWS). It is a biannual publication (November and June) focusing on developments in global food markets. Food Outlook maintains a close synergy with another major GIEWS publication, Crop Prospects and Food Situation, especially with regard to the coverage of cereals. Food Outlook is available in English. The summary section is also available in Arabic, Chinese, French, Russian and Spanish
Meat Market Review: Price and policy update, August 2020
23/08/2020
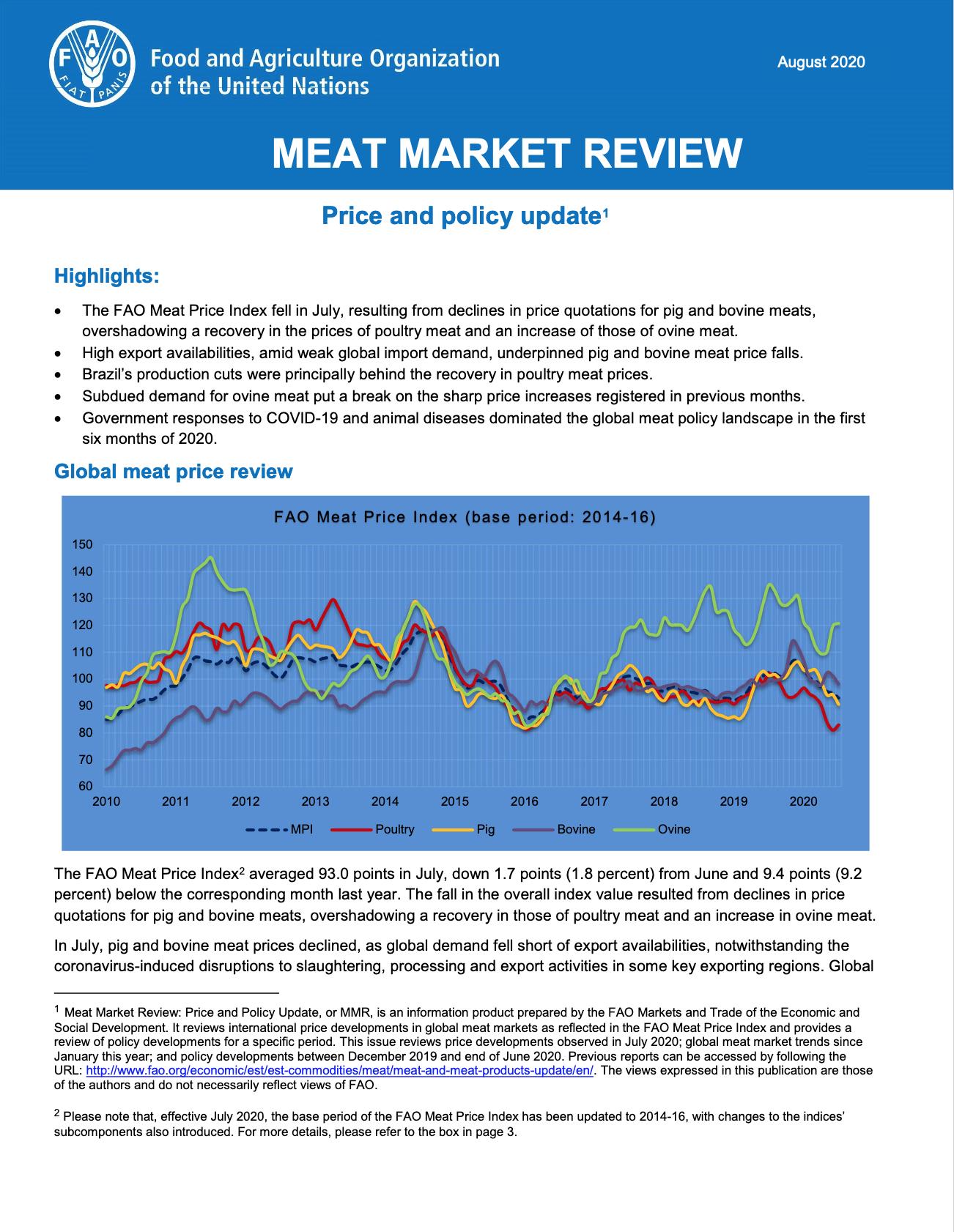
The FAO Meat Price Index fell in July, resulting from declines in price quotations for pig and bovine meats, overshadowing a recovery in the prices of poultry meat and an increase of those of ovine meat. High export availabilities, amid weak global import demand, underpinned pig and bovine meat price falls. Brazil’s production cuts were principally behind the recovery in poultry meat prices. Subdued demand for ovine meat put a break on the sharp price increases registered in previous months. Government responses to COVID-19 and animal diseases dominated the global meat policy landscape in the first six months of 2020.
Oilseeds, Oils & Meals. Monthly Price and Policy Update No.133, August 2020
19/08/2020
The month of July saw FAO’s price indices for oilseeds and vegetable oils rise to multi-month highs, gaining, respectively, 3.1 and 6.6 points (or 3.5 and 7.6 percent). By contrast, in the case of oilmeals, the price index only marginally recovered from the marked falls registered in May and June, up merely 0.5 points (or 0.6 percent) in July. Compared to their year-earlier levels, the oilseeds and oilmeals indices stood, respectively, 4 and 2 percent above the respective July 2019 values, while the vegetable oils index registered a remarkable advance of 19 percent year-on-year.

No. 35 Trade finance and digital technologies: Facilitating access to international markets
07/08/2020
This policy brief provides an overview of how digital technologies can help facilitate access to trade finance for market participants, in particular micro, small and medium sized enterprises, by addressing numerous challenges in traditional trade finance.
Oilseeds, Oils & Meals. Monthly Price and Policy Update No.132, July 2020
15/07/2020
In June, FAO’s price index for oilseeds recovered moderately from the nine-month low observed in May, gaining 2.0 points (or 2.3 percent). Mean-while, the vegetable oils index saw a marked rebound after declining for four months in a row, climbing by 8.8 points (or 11.3 percent) from its May value. By contrast, the oilmeal index continued declining, shedding 1.9 points (or 2.3 percent) month-on-month and reaching a six-month low. While the indices for both oilseeds and vegetable oils stood above their year-earlier levels, the index for oilmeals fell below the level recorded in the corresponding month of last year.

GIEWS Update - South America, 15 July 2020
15/07/2020
In late May 2020, a locust outbreak was reported in northeastern provinces of Formosa, Santa Fé and Corrientes in Argentina. Crop and pasture losses have been limited due to the implementation of effective control measures. If swarms move to key producing areas of Argentina, Brazil and Uruguay, they could threaten the main 2020 winter wheat and barley crops that will be harvested in the last quarter of the year. Intensification of surveillance and treatment activities are required to contain the situation and avoid significant crop losses.
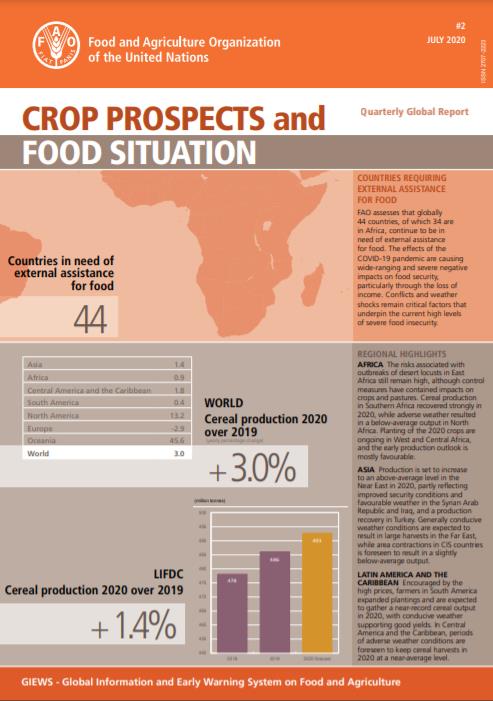
Crop Prospects and Food Situation - Quarterly Global Report, No. 2, July 2020
02/07/2020
FAO assesses that globally 44 countries, of which 34 are in Africa, continue to be in need of external assistance for food. The effects of the COVID-19 pandemic are causing wide‑ranging and severe negative impacts on food security, particularly through the loss of income. Conflicts and weather shocks remain critical factors that underpin the current high levels of severe food insecurity.

Cereal supply and demand balances for sub-Saharan African countries - No.2, July 2020
02/07/2020
The FAO/GIEWS Country Cereal Balance System (CCBS) is a database of annual supply and utilization balances for main cereals, covering all countries of the world. Since 1980, the FAO/GIEWS team maintains and updates it continually. This statistical report contains a subset of CCBS data and presents updated cereal supply and demand balances for all sub-Saharan African countries. It complements the information of the FAO/GIEWS Crop Prospects and Food Situation report and is published four time a year with the same schedule.

Review of agricultural trade policies in post-Soviet countries 2017–2018
25/06/2020
The publication presents analysis of agricultural trade policies in post-Soviet countries. The aim of the review is to monitor the latest changes in trade policies of these countries, affecting the dynamics and structure of trade. The publication includes a chapter with an overview of the prospects for expanding the agricultural trade of some Central Asian countries with China and the Russian Federation, and a chapter about the impact of climate change on agricultural trade in Eastern Europe and Central Asia.
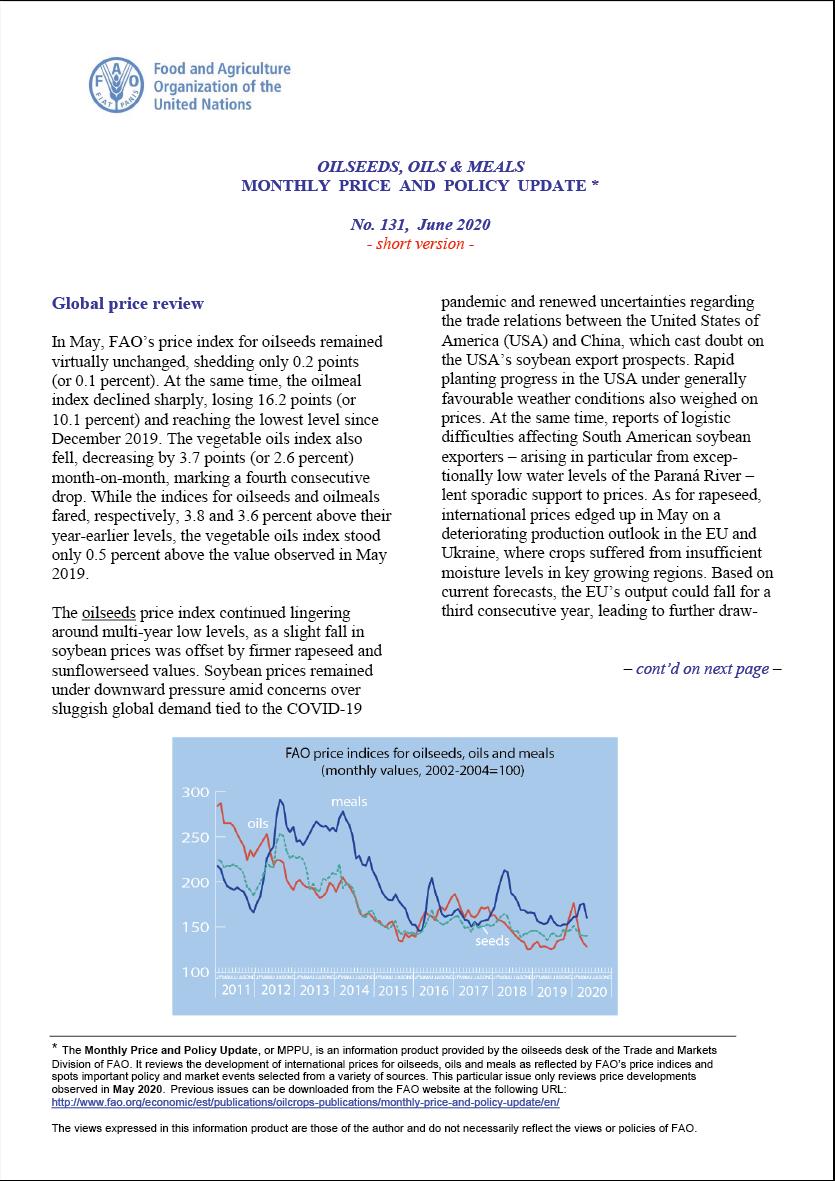
Oilseeds, Oils & Meals. Monthly Price and Policy Update No.131, June 2020
17/06/2020
In May, FAO’s price index for oilseeds remained virtually unchanged, shedding only 0.2 points(or 0.1 percent). At the same time, the oilmeal index declined sharply, losing 16.2 points (or10.1 percent) and reaching the lowest level since December 2019. The vegetable oils index also fell, decreasing by 3.7 points(or 2.6 percent) month-on-month, marking a fourth consecutive drop. While the indices for oilseeds and oilmeals fared, respectively, 3.8 and 3.6 percent above their year-earlier levels, the vegetable oils index stood only 0.5 percent above the value observed in May 2019.
Food Price Monitoring and Analysis (FPMA) Bulletin # 5, 10 June 2020
10/06/2020
Export prices of wheat dipped in May after an increase in April, pressured by a good supply outlook and a slow pace in trade. Prices of maize declined further on large export availabilities amid weak import demand. By contrast, international prices of rice increased for the fifth consecutive month. In East Africa, disruptions to food supply chains and stronger demand triggered by the COVID-19 pandemic continued to underpin sharp food price increases in May in Somalia, the Sudan and South Sudan. In Southern Africa, prices of maize declined in May with the arrival of the 2020 harvests, which are estimated to have recovered from last year’s reduced levels in several countries. In East Asia and South America, the slowdown in domestic buying and improved availabilities from the new harvests halted the sharp increases in the prices of rice of the past few months that were triggered by the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.

Major tropical fruits - Statistical compendium 2018
09/06/2020
The Major Tropical Fruits Statistical compendium, issued once a year, contains information on global trade in mangoes, pineapples, avocados and papayas. Its sources include information provided by FAO member nations, traders, news bulletins and the opinions of commodity specialists and represents the most authoritative and up-to-date source of information on the world tropical fruit economy.
